
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is a substitute to standard open surgical techniques performed to treat different spinal disorders, like degenerative disc disease, herniated disc, scoliosis, and spinal stenosis. Minimally invasive spine surgery offers several promising benefits, including smaller incisions, outpatient alternatives, less post-operative pain, and a quicker recovery.
Types of surgical techniques performed minimally invasively include:
• Discectomy or Microdiscectomy
• Foraminotomy or Microforaminotomy
• Microlaminectomy and Microlaminotomy

Treatment of a spinal fracture caused by osteoporosis is generally two-pronged, involving both treatment of the fracture, and treatment of the underlying osteoporosis which led to the fracture.
• Vertebroplasty - This minimally invasive treatment is devised to help lower or eliminate pain caused by a fractured vertebra and balance the bone. Low viscosity cement is administered directly into the contracted vertebral body under the pressure, with the aim of balancing the fracture and easing the related back pain.
• Kyphoplasty - Identical to vertebroplasty, kyphoplasty is a minimally invasive technique devised to lower or stop the pain caused by a spinal fracture, to balance the bone, and to restore certain or all of the lost vertebral body height caused by the compression fracture.
• Spinal Fusion Surgery - Spinal fusion surgery is sometimes used for spinal compression fractures to terminate movement between two vertebrae and ease pain. The technique joins two or more vertebrae together, holds them in the right position, and keeps them from moving until they have a chance to grow together, or join.
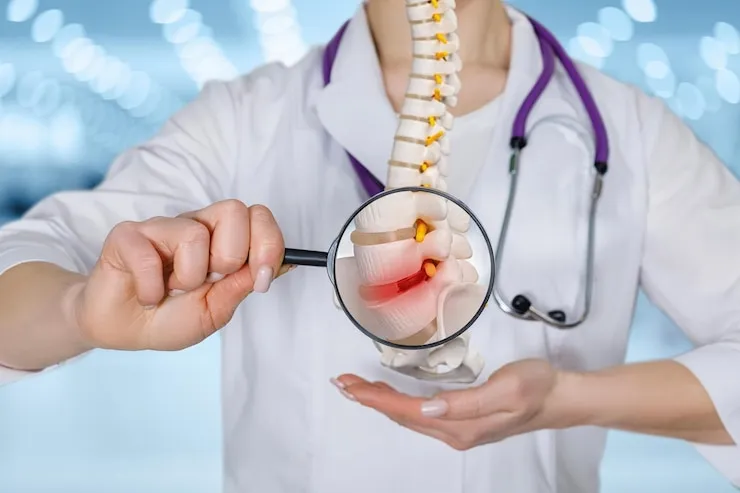
A Spinal fusion permanently joins two or more vertebrae to improve stability, correct deformities, or reduce pain. Your primary care physician might recommend a spinal fusion to treat:
• Deformities of the spine - Spinal fusion could help correct spinal deformities, like a sideways curvature of the spine otherwise known as scoliosis.
• Spinal weakness or instability - Your spine might become unbalanced if there is abnormal or excessive movement between 2 vertebrae. These are common side effects of serious arthritis in the spine. A spinal fusion is used to restore spinal stability in such cases.
• Herniated disc - Spinal fusion might be used to balance the spine after the removal of a damaged herniated disc.
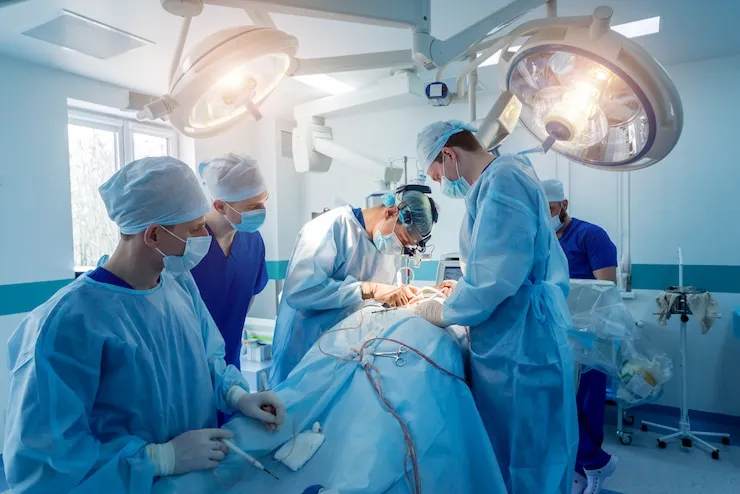
Scoliosis, spondylolisthesis, and kyphosis are commonly treated with spinal reconstructive surgery. Neurosurgeons use minimally invasive surgery, artificial disc replacement, endoscopy, kyphoplasty, spinal fusion, and other surgical techniques depending upon the needed care.
Spinal reconstructive surgery might be required for patients who have a misalignment that affects a majority of the spine.